Key Questions Answered in this Section
- What are the major crops contributing to biomass feedstock production in Uttar Pradesh?
- Which regions in Uttar Pradesh are known for cultivation of prominent crops?
- Which types of biomass residues are generated in Uttar Pradesh?
- What are the biomass clusters in Uttar Pradesh?
- How is the biomass supply chain in Uttar Pradesh?
- How much wheat straw is generated in Uttar Pradesh?
- How much rice husk is generated in Uttar Pradesh?
- How much rice straw is generated in Uttar Pradesh?
- How much sugarcane bagasse is generated in Uttar Pradesh?
- How much sugarcane trash is generated in Uttar Pradesh?
- How much bajra stalk is generated in Uttar Pradesh?
Uttar Pradesh comprises a mix of urban and rural regions, with the top urban areas being Lucknow, Kanpur, Ghaziabad, Agra, Varanasi, Meerut, Prayagraj, Bareilly, Aligarh, and Moradabad. Understanding the biomass supply chain in Uttar Pradesh is crucial for optimizing the utilization of agricultural residues and enhancing the state’s bioenergy potential.
Major Crops Grown in Uttar Pradesh
The crops associated with biomass feedstock generation in Uttar Pradesh include:
| Crop | Total Production (MTPA) |
| Sugarcane | 177 |
| Wheat | 34 |
| Rice | 15 |
| Bajra | 1.95 |
| Mustard | 1 |
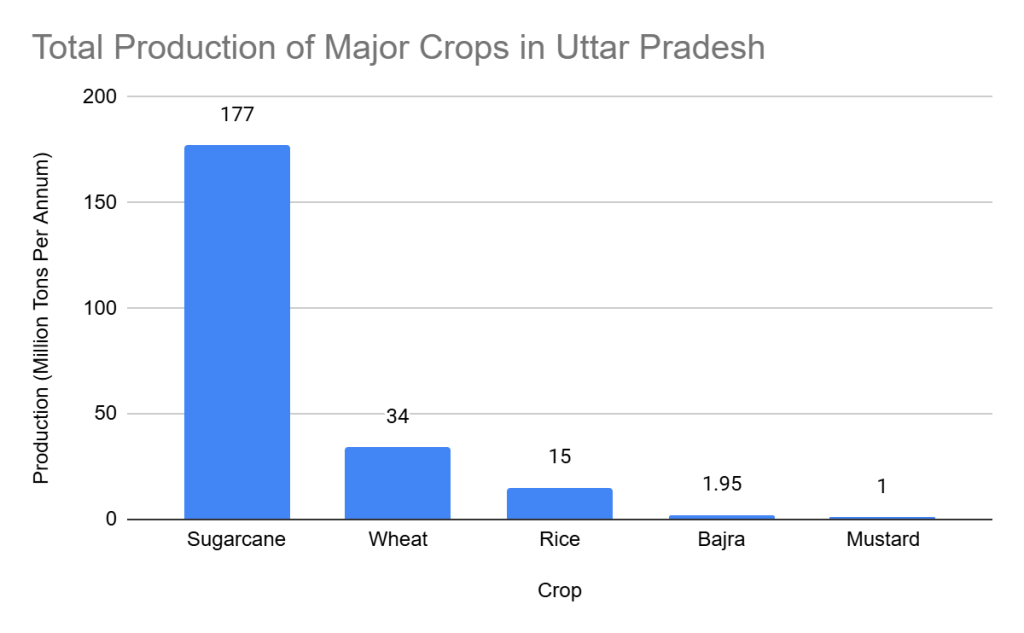
The cultivation of these crops results in substantial biomass feedstock, contributing significantly to Uttar Pradesh’s bioeconomy.
Residue Generation in Uttar Pradesh
For each crop, the total residue generation data is as follows:
| Crop | Residue Type | Quantity (MTPA) |
| Wheat | Straw | 26 |
| Rice | Husk, Straw | 25.2 |
| Sugarcane | Bagasse, Trash | 63.7 |
| Bajra | Stalk | – |
Efficient management of these crop residues is essential for developing a sustainable biomass supply chain in Uttar Pradesh.
Significant Regions of Availability in Uttar Pradesh
The regions within Uttar Pradesh with significant availability of each crop’s biomass residues are:
- Wheat: Western UP, including regions like Agra, Meerut.
- Rice: Bijnor, Kushinagar, Pilibhit, Chandauli, Baghpat, Varanasi.
- Sugarcane: Meerut, Bareilly, Saharanpur, Bulandshahr.
Identifying these biomass clusters enables targeted strategies for biomass feedstock collection and utilization. Each region’s unique crop profile contributes to the diversity of agricultural residues, impacting the overall biomass availability in Uttar Pradesh.
Utilization of Crop Residues at the Farmer’s Level in Uttar Pradesh
- Essential Usage for Livestock and Fertilizer
- Residues of Rice and Moong are commonly used as cattle feed.
- Residues from Rice, Moong, and oilseeds are processed into compost fertilizers.
- Specific Usage in Construction and Agriculture
- Arhar stalks are utilized for building small huts.
- Soybean residues are used as fuel in brick kilns.
- Sugarcane top leaves serve as cattle feed, while bagasse is employed for energy generation in sugar mills.
- Banana residues are used in organic mushroom production.
- Fuel Usage for Domestic Needs
Stalks of Arhar, Cotton, and Mustard are used as fuel for domestic cooking. - Field Preparation through Residue Burning
Open burning of residues from Garlic, Cotton stalks, Rapeseed & Mustard, Rice, and Wheat is commonly practiced for preparing fields for the next crop cycle. - Commercial Applications
Farmers earn additional income by selling crop residues to briquetting or biomass plants, adding value to agricultural byproducts.

