Key Questions Answered in this Section
- Which crops contribute most significantly to biomass feedstock generation in Maharashtra?
- Which regions in Maharashtra are the primary hubs for biomass residue availability?
- What are the biomass clusters in Maharashtra?
- How is the biomass supply chain in Maharashtra?
- What are the major types of biomass residues available in Maharashtra, and how are they generated?
- How much sugarcane bagasse and cane trash is generated in Maharashtra?
- How much maize cob and husk is generated in Maharashtra?
- How much cotton stalk is generated in Maharashtra?
- How much soybean stalk is generated in Maharashtra?
- How much wheat straw is generated in Maharashtra?
- How much cashew nut shells is generated in Maharashtra?
- How much groundnut shells is generated in Maharashtra?
Maharashtra comprises a mix of urban and rural regions, with the top urban areas being Mumbai, Pune, Nagpur, Thane, Nashik, Vasai-Virar, Aurangabad, Solapur, Bhiwandi, and Amravati. Understanding the biomass supply chain in Maharashtra is crucial for optimizing the utilization of agri residues and enhancing the state’s bioenergy potential.
Major Crops Grown
| Crop | Production (Million Tons Per Annum) |
| Sugarcane | 110 |
| Bamboo | 26.5 |
| Cotton | 7 |
| Soybean | 5.5 |
| Maize | 3.5 |
| Gram | 3.3 |
| Wheat | 2.47 |
| Jowar | 1.7 |
| Tur | 1.37 |
| Bajra | 0.48 |
| Groundnut | 0.38 |
| Cashew | 0.2 |
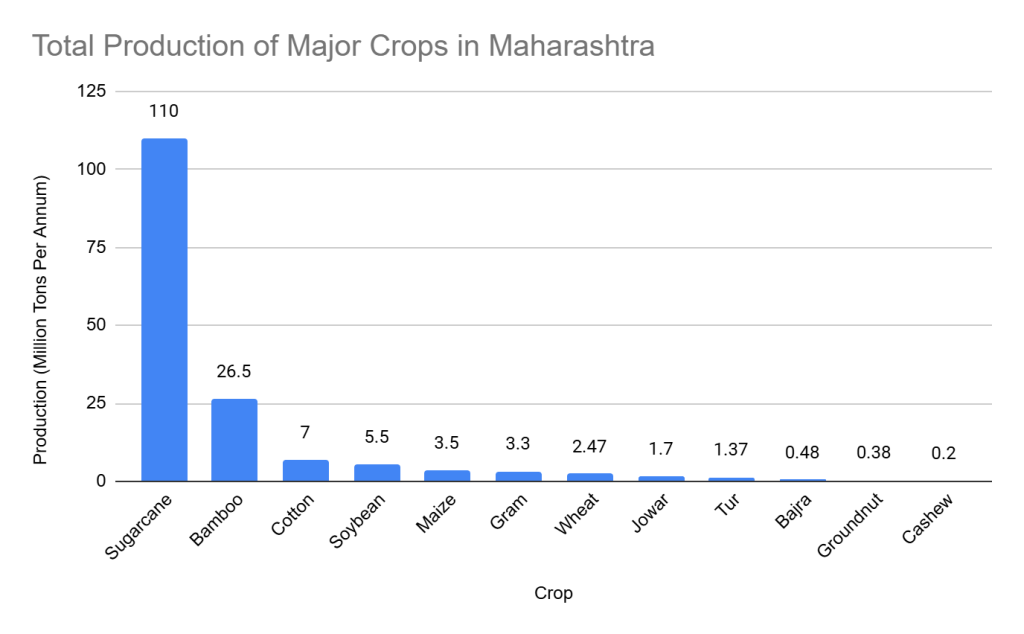
The cultivation of sugarcane, cotton, soybean, and wheat results in substantial biomass feedstock, contributing significantly to Maharashtra’s bioeconomy.
Residue Generation
| Crop | Residue Type | Total Generation (Million Tonnes Per Annum) |
| Sugarcane | Bagasse, Cane Trash | 39.6 |
| Maize | Cob, Husk | 1.75 |
| Cotton | Stalk | 3.5 |
| Soybean | Stalk | 2.47 |
| Wheat | Straw | 0.8 |
| Cashew Nut | Shell | 0.14 |
| Groundnut | Shell | 0.11 |
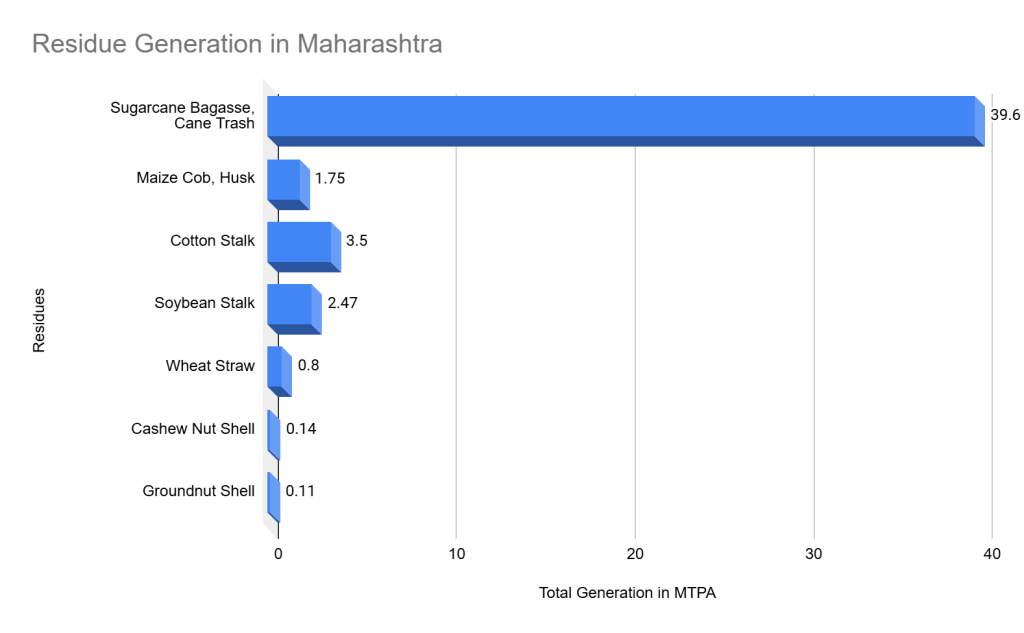
Efficient management of these crop residues is essential for developing a sustainable biomass supply chain in Maharashtra.
Significant Regions of Availability
- Sugarcane: Pune, Satara, Solapur, Ahmednagar, Aurangabad
- Maize: Siddipet, Kolhapur, Satara, Pune
- Soybean: Yavatmal, Amravati, Buldhana, Nagpur, Wardha, Chandrapur
- Cotton: Nagpur, Aurangabad, Jalna
- Cashew: South Konkan Region (Rajgad and Ratnagiri districts), Sindhudurg, Thane, Palghar
- Bamboo: Konkan, Western Ghat, Sindhudurg, Palghar, Thane, Raigad, Ratnagiri
- Wheat: Ahmadnagar, Nashik, Pune, Solapur, Jalgaon, Satara, Dhule, Sangli, Kolhapur
Identifying these biomass clusters enables targeted strategies for biomass feedstock collection and utilization.
Prominent Crops in Different Regions of Maharashtra
| Region | Prominent Crops |
| Pune | Sugarcane, Maize, Wheat |
| Satara | Sugarcane, Maize, Wheat |
| Solapur | Sugarcane, Wheat, Jowar |
| Ahmednagar | Sugarcane, Wheat, Jowar |
| Aurangabad | Sugarcane, Cotton, Paddy, Maize, Wheat |
| Siddipet | Maize, Paddy, Castor |
| Kolhapur | Maize, Wheat, Sugarcane |
| Yavatmal | Soybean, Cotton, Jowar |
| Amravati | Soybean, Cotton, Pigeonpea |
| Buldhana | Soybean, Jowar, Maize |
| Nagpur | Soybean, Cotton, Wheat |
| Wardha | Soybean, Pigeonpea, Cotton |
| Chandrapur | Soybean, Paddy, Cotton |
| Jalna | Cotton, Jowar, Wheat |
| South Konkan Region | Cashew, Paddy, Mango, Coconut |
| Sindhudurg | Cashew, Bamboo, Coconut |
| Thane | Cashew, Bamboo, Paddy |
| Palghar | Cashew, Bamboo, Paddy, Millet, Black Gram |
| Raigad | Bamboo, Rice, Millet |
| Ratnagiri | Bamboo, Cashew, Coconut |
| Nashik | Wheat, Rice, Jowar |
| Jalgaon | Wheat, Tea, Cotton |
| Dhule | Wheat, Cotton, Jowar |
| Sangli | Wheat, Jowar, Maize |
Each region’s unique crop profile contributes to the diversity of agricultural residues, impacting the overall biomass availability in Maharashtra.
Utilization of Crop Residues at the Farmer’s Level in Maharashtra
- Essential Usage for Livestock
Crop residues from Bajra, Gram, Groundnut, Green gram, Jowar, Maize, Ragi, and Wheat are widely used as cattle feed. Additionally, Soybean husk and Arhar husk are also utilized for this purpose. - Organic Fertilizer Preparation
Residues from crops like Arhar, Bajra, Chia seed, Jowar, Green gram, Groundnut, Chilies, Moth beans, and Shatavari are commonly used to prepare compost fertilizers. - Specific Usage in Construction and Energy
- Arhar stalks are used for constructing small huts.
- Soybean residue serves as fuel for brick kilns.
- Sugarcane top leaves are fed to cattle, and bagasse is utilized for energy generation in sugar mills.
- In districts like Bhandara and Nagpur, rice residues are processed to create raw material for incense sticks.
- Fuel Usage for Domestic Purposes
Cotton stalks and Arhar stalks are often used as fuel for domestic cooking in traditional chulhas. - Field Preparation through Residue Burning
Cotton stubbles are burned in fields to prepare seedbeds for the next sowing season. - Commercial Applications
Crop residues are sold to briquetting or biomass plants, enabling farmers to earn additional revenue from these materials.

