Key Questions Answered in this Section
- What are the major crops contributing to biomass feedstock production in Andhra Pradesh?
- Which regions in Andhra Pradesh are known for cultivation of prominent crops?
- Which types of biomass residues are generated in Andhra Pradesh?
- What are the biomass & agri residue clusters in Andhra Pradesh?
- How is the biomass supply chain in Andhra Pradesh?
- How much rice straw is generated in Andhra Pradesh?
- How much rice husk is generated in Andhra Pradesh?
- How much sugarcane trash is generated in Andhra Pradesh?
- How much sugarcane bagasse is generated in Andhra Pradesh?
- How much maize cob is generated in Andhra Pradesh?
- How much maize husk is generated in Andhra Pradesh?
- How much castor seed shells are generated in Andhra Pradesh?
- How much cashew nut shells are generated in Andhra Pradesh?
Andhra Pradesh comprises a mix of urban and rural regions, with the top urban areas being Visakhapatnam, Vijayawada, Guntur, Nellore, Kurnool, Rajahmundry, Kakinada, Tirupati, Kadapa, and Anantapur. Andhra Pradesh’s combination of thriving urban centers and extensive rural agricultural areas creates significant opportunities for biomass production from agricultural residues. Understanding the biomass supply chain in Andhra Pradesh is crucial for optimizing the utilization of agri residues and enhancing the state’s bioenergy potential.
Expert Consulting Assistance for Indian Bioenergy & Biomaterials
Talk to BioBiz
Call Muthu – 9952910083
Email – ask@biobiz.in
Major Crops Grown in Andhra Pradesh
The crops associated with biomass feedstock generation in Andhra Pradesh include:
| Crop | Total Production (MTPA) |
| Rice | 7.8 |
| Sugarcane | 3.65 |
| Maize | 2 |
| Cotton | 1.7 |
| Castor seed | 0.09 |
| Cashew Nut | 0.12 |
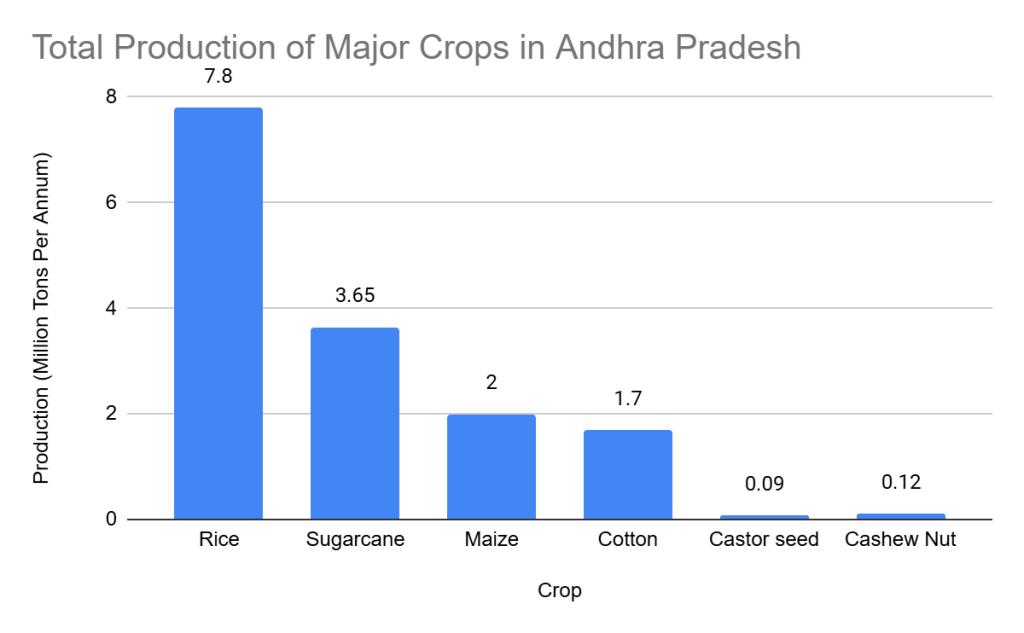
The cultivation of these crops results in substantial biomass feedstock, contributing significantly to Andhra Pradesh’s bioeconomy.
Residue Generation in Andhra Pradesh
For each crop, the total residue generation data is as follows:
| Crop | Residue Type | Quantity (MTPA) |
| Rice | Straw, husk | 13.1 |
| Sugarcane | Trash, bagasse | 1.3 |
| Maize | Cob, husk | 0.6 |
| Castor seed | Seed Shells | 0.02 |
| Cashew nut | Shells | 0.08 |
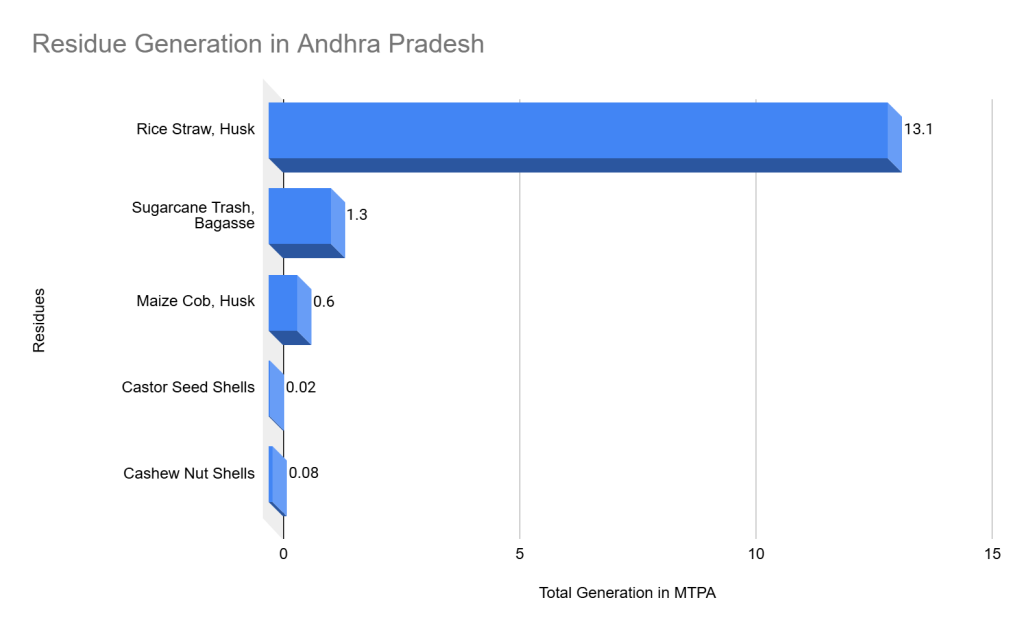
Efficient management of these crop residues is essential for developing a sustainable biomass supply chain in Andhra Pradesh.
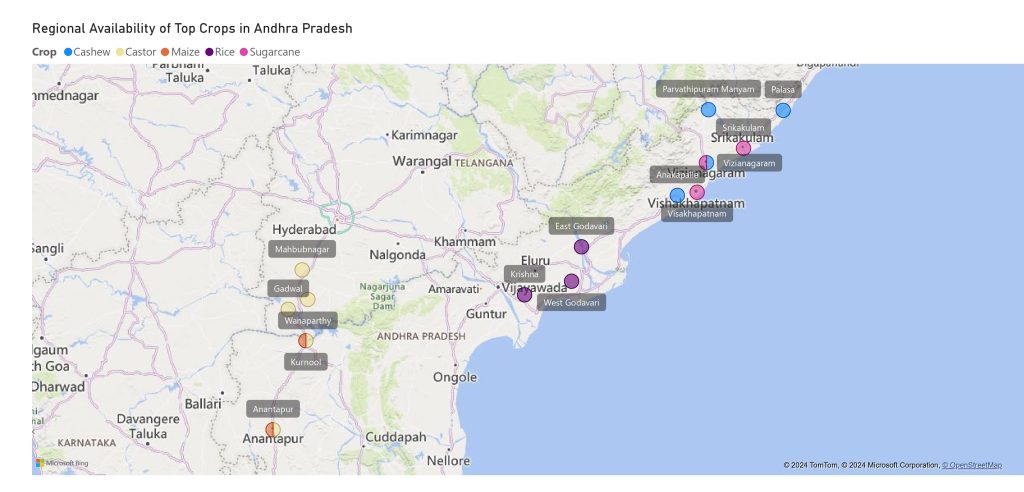
Significant Regions of Availability in Andhra Pradesh
Regions in Andhra Pradesh with significant availability of crop residues:
- Rice: East Godavari, West Godavari, Krishna
- Sugarcane: Srikakulam, Vizianagaram and Visakhapatnam.
- Maize: Kurnool, Anantapur
- Castor: Ananthapur, Kurnool, Mahbubnagar, Wanaparthy, and Gadwal.
- Cashew: Palasa, Vizianagaram, Parvathipuram Manyam, Anakapalle
Identifying these biomass clusters enables targeted strategies for biomass feedstock collection and utilization
Prominent Crops in Different Regions of Andhra Pradesh
Each region’s unique crop profile contributes to the diversity of agricultural residues, impacting the overall biomass availability in Andhra Pradesh.
| Region | Prominent Crops |
| East Godavari | Rice |
| West Godavari | Rice |
| Krishna | Rice |
| Srikakulam | Sugarcane |
| Vizianagaram | Sugarcane, Cashew |
| Visakhapatnam | Sugarcane |
| Kurnool | Maize, Castor |
| Anantapur | Maize, Castor |
| Mahbubnagar | Castor |
| Wanaparthy | Castor |
| Gadwal | Castor |
| Palasa | Cashew |
| Parvathipuram Manyam | Cashew |
| Anakapalle | Cashew |
Utilization of Crop Residues at the Farmer’s Level in Andhra Pradesh
- Essential Usage for Livestock and Fertilizer
- Residues of Arhar, Groundnut, Rice, and Maize are extensively used as cattle feed.
- Residues from Dry Chili, Groundnut, and oilseeds are predominantly used for composting (manure preparation).
- Fuel Usage for Domestic Needs
Crop residues such as Arhar, Cotton, Sunflower, and Wheat are utilized as fuel for domestic cooking. - Field Preparation through Residue Burning
Stubbles from Arhar, Cotton, Sunflower, Sugarcane, and Rice are often burned openly to prepare fields for the next crop cycle. - Special Usage in Sustainable Farming
- Some farmers practice mulching, where crop residue is used to suppress weeds and reduce water loss through evaporation.
- Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF) is practiced by avoiding chemical fertilizers and utilizing crop residues effectively.
- Commercial Applications
Farmers earn revenue by selling crop residues to briquetting or biomass plants, providing an economic value for agricultural waste.

