Key Questions Answered in this Section
- What are corn husks, and why are they considered a valuable biomass feedstock?
- How much corn husk is generated annually in India, and which states contribute the most to this production?
- What are the main characteristics of corn husks that make them suitable for energy applications?
- What are the current and emerging uses of corn husks in industries and agriculture?
- What are the challenges associated with storing and processing corn husks for industrial use?
- How are corn husks processed for industrial heating and power generation?
- What forms of corn husks (e.g., pellets, briquettes) are most commonly used in industrial applications?
- What types of boilers are used for utilizing corn husks, and what are their efficiency levels?
- Which industries in India are the primary consumers of corn husks for energy and heating?
- What is the current utilization rate of corn husks in Indian industries, and how is this expected to grow?
- How is the price of corn husks in loose form and briquette form determined, and what factors influence its cost?
- Is it possible to directly use corn husk in boilers?
Introduction
Corn husks, the leafy outer coverings of corn ears, are an abundant and versatile biomass feedstock with high cellulose content. Traditionally considered agricultural waste, these husks are now prized for their potential in bioethanol production, biogas, and sustainable packaging materials.
Expert Consulting Assistance for Indian Bioenergy & Biomaterials
Talk to BioBiz
Call Muthu – 9952910083
Email – ask@biobiz.in
Corn husks decompose readily, making them suitable for biochar, compost, and even as animal feed. Beyond energy, their fibers are processed into biodegradable plastics, paper, and textiles, offering eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic materials.
Let us look into the price, availability, and proximate analysis of corn husk briquettes and pellets, their use in boilers, and the role of transport and logistics in their efficient distribution.
Total Corn Husk Generation in India
India produces 33 million tonnes of maize plant annually. It is said that husks make up 14% of the total maize plant weight. So, the total corn husk generation is about 4.6 million tonnes. Assessing the availability of corn husk involves analyzing its proximate analysis to determine suitability for various applications.
Biomass Characteristics
The table summarizes proximate analysis (moisture, volatile matter, ash, fixed carbon) and feedstock costs, highlighting quality and economic feasibility. The proximate analysis of corn husk reveals its efficiency when used in boilers, highlighting its potential as a renewable energy source.
| Parameter | Value (For Pellets) |
| Gross Calorific Value (GCV) | 4200 Kcal/kg |
| Moisture Content | 8% |
| Ash Content | 2% |
| Silica Content | 2-5% |
| Volatile Matter | 78% |
| Fixed Carbon | 10.5% |
| Bulk Density | 244-304 Kg/m3 |
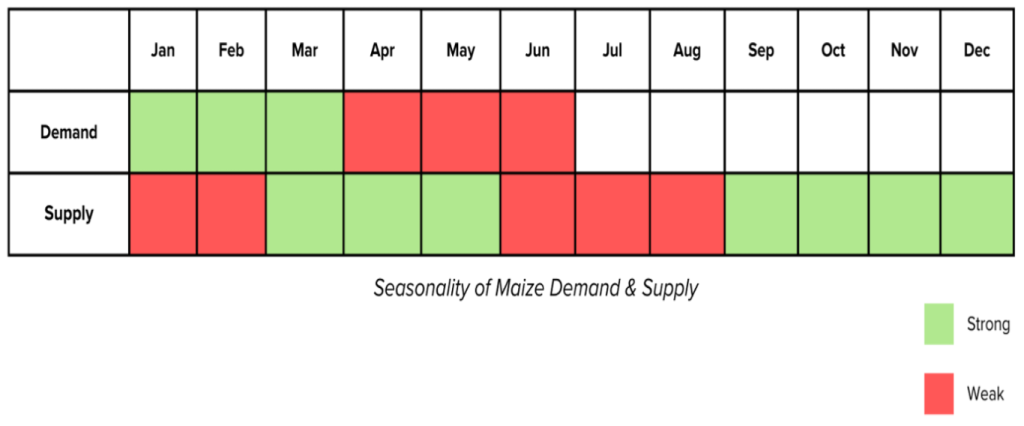
Seasonality
- Kharif season is the main growing season in northern India. In the south, however, maize is sown any time from April to October.
- Kharif maize represents around 83% of the maize area in India, while rabi maize corresponds to 17% maize area. Over 70% of the Kharif maize area is grown under rainfed conditions with a prevalence of many biotic and abiotic stresses.
Regional Availability
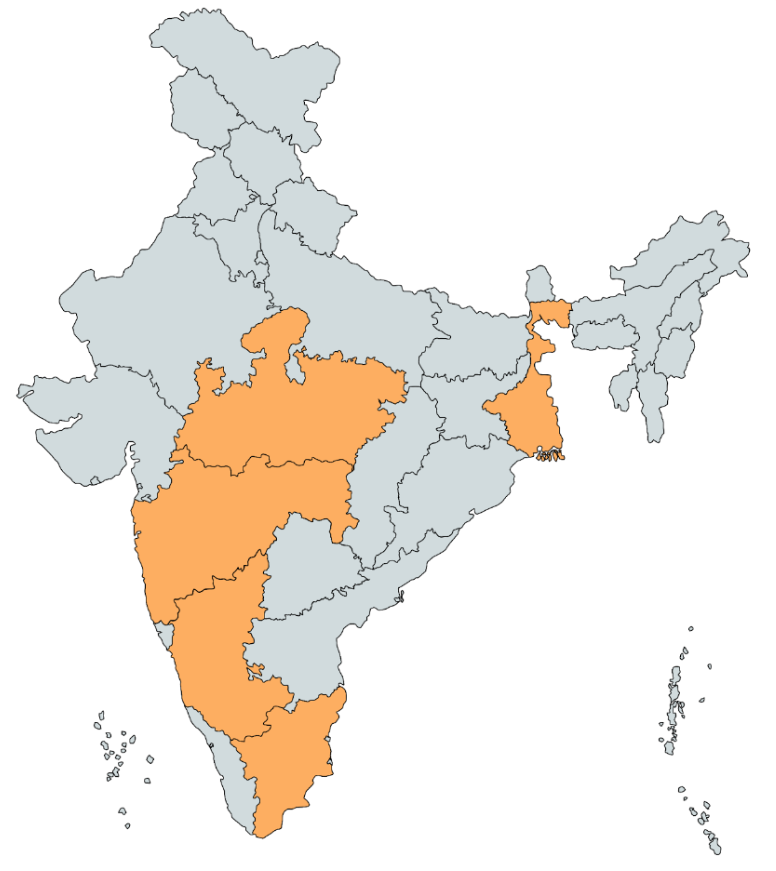
Regions with abundant corn husk availability can leverage this resource for use in boilers, promoting sustainable energy practices. The following are the top five states in India where maize/corn cobs are abundantly available, along with key regions within those states:
| State | Total Crop Production in MTPA | Total Corn Cob Generation (MTPA) | Key Regions |
| Karnataka | 5 | 2.3 | Shimoga, Davangere, Chitradurga |
| Madhya Pradesh | 4.5 | 2.07 | Chhindwara, Seoni, Betul, Barwani, Dhar |
| Maharashtra | 3.5 | 1.6 | Siddipet, Kolhapur, Satara, Pune |
| Tamilnadu | 2.8 | 1.3 | Salem, Dindigul, Namakkal, Pudukottai, Tiruppur, Villuppuram, Perambalur, Ariyalur |
| West Bengal | 2.6 | 1.2 | Nadia, Malda, Murshidabad, South Dinajpur, Darjeeling |
Uses of Corn Husk
Current Uses
- Bioethanol Production: Corn husks are rich in cellulose, which can be converted into bioethanol, an alternative fuel source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Composting Material: Due to their organic nature, corn husks are commonly composted, enhancing soil fertility and supporting sustainable farming practices.
- Animal Feed: After proper processing, corn husks can be used as livestock feed, providing a low-cost, fibrous supplement in animal diets.
- Handcrafted Goods: In many cultures, corn husks are traditionally used to make artisanal items, such as corn husk dolls, baskets, and mats, contributing to local economies and cultural heritage.

Emerging Uses
- Biodegradable Packaging: Researchers are developing corn husk-based materials for biodegradable packaging, offering a sustainable alternative to plastic.
- Natural Fiber Textiles: Corn husk fibers are being explored for use in eco-friendly textiles, creating fabric blends that are sustainable and compostable.

- Biochar for Soil Amendment: Biochar made from corn husks is emerging as a soil amendment that improves soil health, aids in water retention, and sequesters carbon.
- Activated Carbon for Filtration: Corn husks are processed into activated carbon, which can be used in water and air filtration systems, offering a low-cost, sustainable filtration solution.
Storage of Corn Husks
- Drying: Corn husks should be thoroughly dried before storage to prevent mold growth and decay. Ideally, they should be sun-dried or air-dried in a well-ventilated area until they are completely moisture-free.
- Moisture Control: Store dried corn husks in a cool, dry place with low humidity to prevent reabsorption of moisture, which can lead to microbial growth. Consider using desiccants or humidity control packs for added moisture protection.
- Ventilated Storage Bins: Use ventilated storage bins or breathable bags (such as burlap) to allow air circulation. Airtight containers are not recommended, as they can trap moisture and accelerate degradation.
- Protection from Pests: Keep corn husks protected from pests by using pest-proof containers, or consider adding natural pest deterrents (like dried bay leaves) to discourage insects and rodents.
- Proper storage ensures that corn husk briquettes and pellets maintain their quality, facilitating efficient transport and logistics to various regions.
Corn Husk as Feedstock – Key Challenges
- High Moisture Content: Corn husks often retain moisture, leading to rapid decomposition and potential mold growth during storage.
- Low Bulk Density: Corn husks have low density, requiring substantial space for storage and increasing transportation costs.
- Processing Complexity: Corn husks may need shredding, drying, and pelletizing to make them suitable for energy or feed applications, adding to processing costs.
- Inconsistent Quality: Variation in nutrient and fiber content complicates its use in animal feed and biofuel production.
Corn Husk for Industrial Heating and Power Generation
Uses of Corn Husks for Industrial Heating and Power Generation
Corn husks can be utilized in several ways within industrial heating and power generation:
- Biomass Fuel: Corn husks are often processed into biomass pellets or briquettes, which can be used in boilers and industrial furnaces for generating heat and steam. This helps in replacing fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Cogeneration: In cogeneration systems, corn husks are combusted to generate electricity while capturing the waste heat for heating applications. This dual-use maximizes efficiency and provides a sustainable energy solution.
- Energy Production: The use of corn husks in anaerobic digestion can produce biogas, which can be harnessed for electricity generation or as a heat source.
- Sustainable Manufacturing Processes: Industries involved in food processing and agriculture can use corn husks for energy, aligning with zero-waste initiatives and improving overall sustainability.
Form in Which Corn Husks Are Used in Industries
In the industrial context, corn husks are predominantly used in the following forms:
- Dried and Chopped: Corn husks are dried and chopped into smaller pieces, making them suitable for direct combustion in industrial boilers.
- Pellets: The husks are processed into pellets, which enhance energy density, improve combustion efficiency, and simplify handling and storage.
- Briquettes: Compressed corn husk briquettes serve as a compact fuel source, ideal for transportation and easy combustion in various heating applications.
- Loose Bulk: In some cases, corn husks are used in their loose form, especially in industries where large quantities are available, like agro-based industries.
Boilers Using Corn Husks
Many industrial boilers are designed to utilize biomass fuels, including corn husks. Key points regarding these boilers include:
- Types of Boilers: The most common types that use corn husks are grate-fired boilers, fluidized bed boilers, and stoker boilers, which can efficiently combust biomass fuels.
- Efficiency: Boilers that use corn husks typically achieve thermal efficiencies ranging from 80% to 90%, depending on the technology used and the quality of the fuel.
- Emission Control: Modern biomass boilers equipped with advanced emission control technologies can significantly reduce particulate matter and other emissions, making them environmentally friendly options.
- Case Studies: Companies like Sanghvi Movers Ltd. in Maharashtra and Nagarjuna Fertilizers have successfully implemented corn husk-fired boilers, showcasing the viability and benefits of using agricultural waste for energy.
Amount of Corn Husks Being Used by Industries for Industrial Heating
The usage of corn husks for industrial heating in India is steadily increasing:
- Statistics: It is estimated that India produces over 30 million tons of corn annually, with around 14% of this weight being husks. This translates to approximately 4.5 million tons of corn husks available for industrial use.
- Industrial Consumption: Reports indicate that industries across India consume nearly 1.5 million tons of corn husks annually for heating and energy production. This figure is projected to grow by 15-20% over the next few years as industries shift towards renewable energy sources.
- Regional Focus: States like Punjab, Haryana, and Maharashtra are leading in the use of corn husks due to their high corn production levels.
Prominent Industries Using Corn Husks for Industrial Heating
Several key industries in India are actively utilizing corn husks for industrial heating and power generation:
- Food Processing: The food industry, particularly corn processing plants, uses husks as fuel for boilers to generate steam and heat.
- Textiles: Textile manufacturers are increasingly adopting biomass fuels, including corn husks, to power their processes sustainably.
- Paper and Pulp: The paper industry uses biomass materials for energy production, with corn husks being an effective alternative to conventional fuels.
- Fertilizer Production: Companies like Coromandel International use corn husks in their production processes, leveraging biomass for energy needs.
- Cement Manufacturing: The cement industry is exploring corn husks as an alternative fuel source, contributing to reducing reliance on coal and fossil fuels.

